Nature-Based tourism: Exploring the Wild, Responsibly
Nature-based tourism, a rapidly growing sector within the global travel industry, offers a unique opportunity to connect with the natural world. It goes beyond simply visiting scenic locations; it emphasizes experiencing and appreciating the environment while contributing to its conservation and the well-being of local communities. This article delves into the intricacies of nature-based tourism, exploring its definitions, principles, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Defining Nature-Based Tourism
Nature-based tourism encompasses a wide range of activities that center around experiencing natural environments. It’s crucial to distinguish it from general tourism that might incidentally involve nature. While a beach vacation or a city park visit might involve elements of nature, nature-based tourism is specifically designed to:

Focus on Natural Attractions: The primary motivation for travel is to experience natural landscapes, wildlife, ecosystems, or cultural practices directly tied to the environment.
Key Principles of Nature-Based Tourism
These principles guide responsible and sustainable practices within the sector:
Sustainability
Minimizing environmental impact: This involves reducing waste, conserving resources, and avoiding disturbance to wildlife and habitats.
Conservation
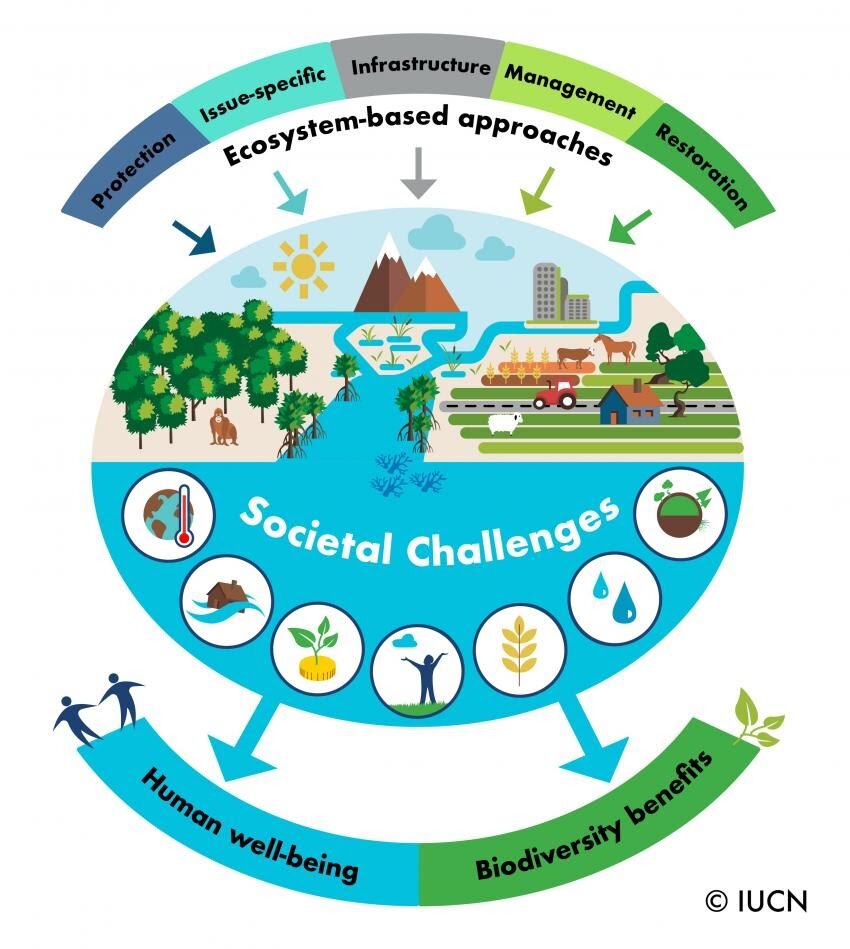
Direct contributions to conservation: This can include funding for protected areas, participation in habitat restoration, and supporting wildlife monitoring programs.
Community Involvement
Local ownership and management: Empowering local communities to participate in the planning and operation of tourism activities.
Education and Interpretation
Providing accurate and engaging information: Helping visitors understand the ecological and cultural significance of the areas they visit.
Diverse Forms of Nature-Based Tourism

Nature-based tourism encompasses a wide array of activities, catering to different interests and levels of adventure. Here are a few examples:
Wildlife Tourism
Safaris: Observing animals in their natural habitats, such as in African game reserves or national parks.
Ecotourism
Hiking and trekking: Exploring natural landscapes on foot.
Adventure Tourism
Mountain climbing: Ascending peaks and experiencing challenging terrain.
Agritourism
Farm stays: Staying at working farms and learning about agricultural practices.
Geotourism
Visiting geological formations: Exploring volcanoes, canyons, and other geological features.
Benefits of Nature-Based Tourism
When practiced responsibly, nature-based tourism can generate numerous benefits:
Environmental Benefits
Conservation of natural resources: Tourism revenue can fund protected area management and conservation programs.
Economic Benefits
Job creation: Tourism creates employment opportunities in rural areas.
Social and Cultural Benefits
Preservation of cultural heritage: Tourism can support the preservation of traditional knowledge and practices.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential benefits, nature-based tourism faces several challenges:
Environmental Impacts
Habitat disturbance: Tourism activities can disrupt wildlife behavior and damage fragile ecosystems.
Socio-Cultural Impacts
Cultural commodification: Tourism can lead to the exploitation of local cultures for commercial gain.
Management Challenges
Lack of infrastructure: Many natural areas lack adequate infrastructure to support tourism activities.
Future Trends in Nature-Based Tourism
The future of nature-based tourism is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
Increased Demand for Authentic Experiences
Travelers are increasingly seeking immersive and meaningful experiences that connect them with nature and local cultures.
Technological Advancements
Use of technology to enhance visitor experiences, such as virtual reality and augmented reality.
Focus on Sustainable Practices
Growing awareness of the importance of responsible tourism.
Community-Based Tourism Growth
Empowering local communities to manage and benefit from tourism.
Regenerative Tourism
Tourism that actively improves the environment and local communities.
Conclusion
Nature-based tourism holds immense potential to contribute to both environmental conservation and sustainable development. By adhering to principles of sustainability, conservation, community involvement, and education, the sector can create positive impacts while providing enriching experiences for travelers. However, it is essential to address the challenges associated with tourism development and ensure that practices remain responsible and ethical. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing the well-being of both people and the planet, nature-based tourism can play a vital role in creating a more sustainable and harmonious relationship between humans and the natural world.



