Nature tourism: A Vital Component of Sustainable Development – UPSC Perspective
Nature tourism, encompassing ecotourism, wildlife tourism, and adventure tourism, has emerged as a significant sector globally, offering both economic opportunities and conservation potential. For UPSC aspirants, understanding the nuances of nature tourism, its impact on the environment and society, and its relevance to sustainable development is crucial. This comprehensive analysis delves into the various facets of nature tourism, examining its potential and challenges within the Indian context.
Nature tourism can be broadly defined as travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and improves the well-being of local people. It emphasizes responsible travel, ethical practices, and minimal impact on the ecosystem.
Ecotourism: A Core Principle
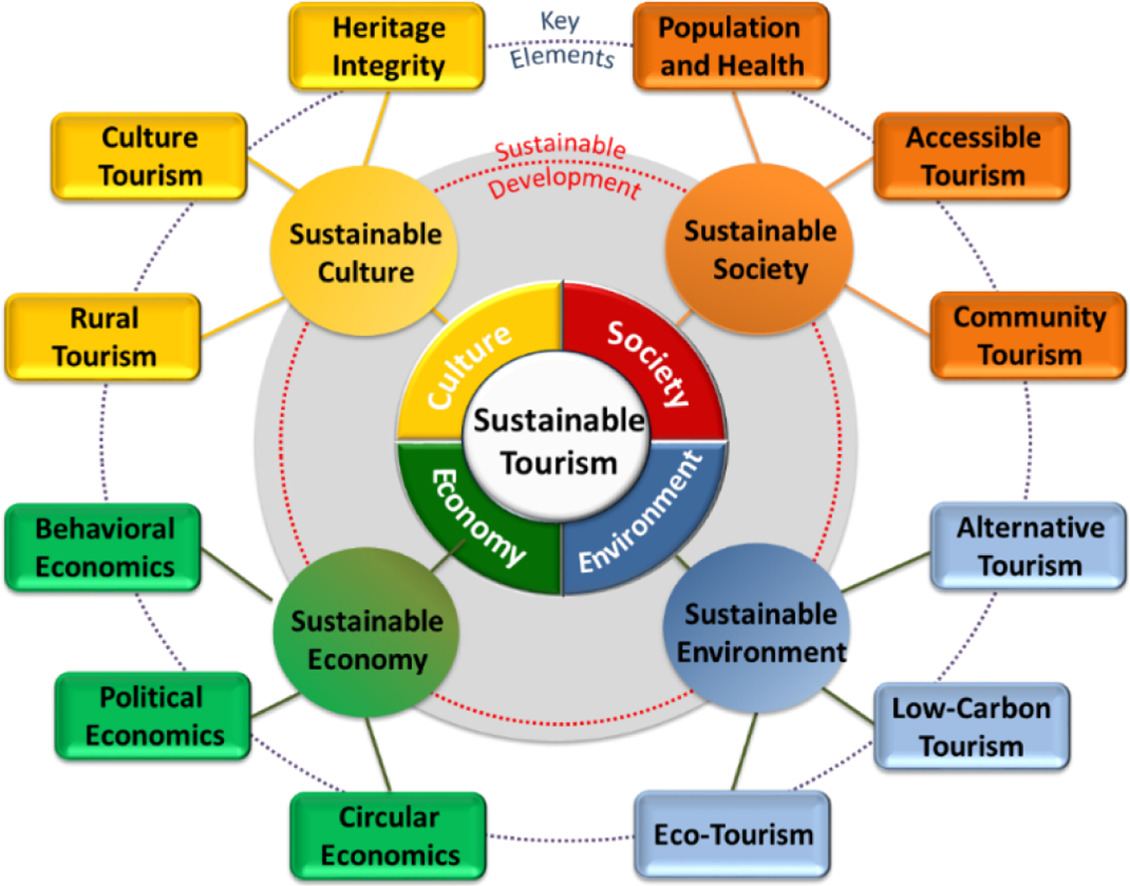
Ecotourism, a subset of nature tourism, prioritizes ecological sustainability and community involvement. It aims to educate travelers about the natural world while contributing to conservation efforts and benefiting local economies.
Wildlife Tourism: Observing Nature’s Majesty
Wildlife tourism focuses on observing and appreciating wildlife in their natural habitats. It includes activities like safaris, birdwatching, and marine life viewing.
Adventure Tourism: Seeking Thrills in Nature
Adventure tourism involves engaging in outdoor activities that offer a sense of excitement and challenge. It includes activities like trekking, mountaineering, rafting, and scuba diving.
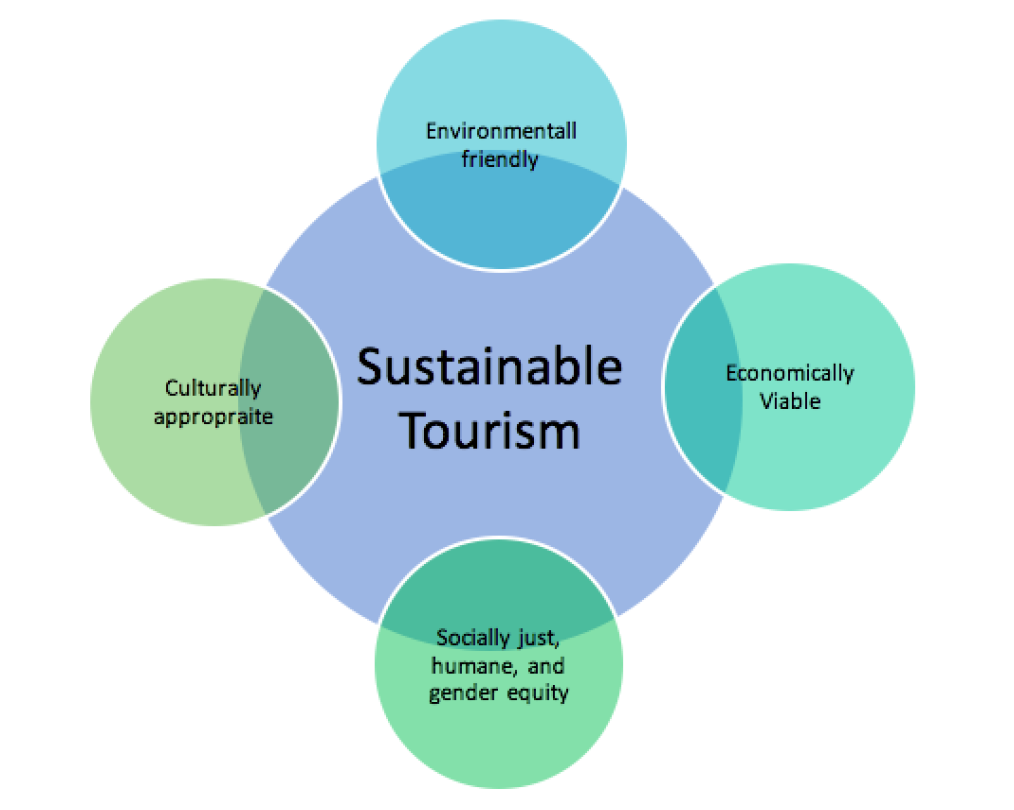
India’s natural heritage is a valuable asset that can drive economic growth and contribute to sustainable development. Nature tourism offers several benefits:
Economic Opportunities and Livelihood Generation
Nature tourism can create employment opportunities for local communities, particularly in remote and rural areas.
Conservation of Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Nature tourism can raise awareness about the importance of conservation and generate funds for protected area management.
Cultural Preservation and Promotion
Nature tourism can promote cultural exchange and understanding between tourists and local communities.
Regional Development and Infrastructure Improvement
Nature tourism can drive infrastructure development, including roads, communication networks, and sanitation facilities, in remote regions.
Despite its potential, nature tourism faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its sustainability.
Environmental Impact and Degradation
Unregulated tourism can lead to habitat destruction, pollution, and disturbance of wildlife.
Socio-Cultural Impacts and Community Displacement
Tourism development can lead to the commodification of local cultures and the loss of traditional values.
Lack of Regulation and Monitoring
Inadequate regulatory frameworks and enforcement mechanisms can lead to unsustainable tourism practices.
Human-Wildlife Conflict
Increased tourist presence in wildlife habitats can increase the frequency and intensity of human-wildlife conflict.
To realize the full potential of nature tourism while mitigating its negative impacts, India needs to adopt a comprehensive and integrated approach.
Strengthening Regulatory Frameworks and Enforcement
Develop and implement clear guidelines and standards for nature tourism activities.
Promoting Community Participation and Benefit Sharing
Involve local communities in the planning and management of nature tourism initiatives.
Enhancing Environmental Awareness and Education
Provide environmental education and interpretation programs for tourists and local communities.
Investing in Infrastructure and Capacity Building
Develop sustainable tourism infrastructure that minimizes environmental impact.
Promoting Responsible Wildlife Tourism
Implement strict guidelines for wildlife viewing and interaction.
Integrating Nature Tourism into Development Planning
Incorporate nature tourism into national and state-level development plans.
UPSC aspirants, as future administrators and policymakers, play a crucial role in promoting sustainable nature tourism in India. They need to:
Understand the complex interrelationships between tourism, environment, and society.
In conclusion, nature tourism holds immense potential for India’s economic growth and sustainable development. By adopting a responsible and integrated approach, India can harness the benefits of its natural heritage while safeguarding its ecological integrity and cultural diversity. The UPSC aspirants must be prepared to tackle the issues associated with nature tourism, and implement solutions that provide the best possible outcome for all stakeholders.


