Navigating the Wild: Unpacking the Multifaceted Objectives of Nature tourism
Nature tourism, a specialized segment of tourism focused on experiencing and appreciating natural environments, has witnessed a surge in popularity in recent decades. While the allure of pristine landscapes and diverse wildlife is undeniable, the objectives driving this form of tourism are far more complex than simple recreation. This exploration delves into the diverse and interconnected objectives of nature tourism, examining its potential for conservation, education, economic development, and cultural preservation.
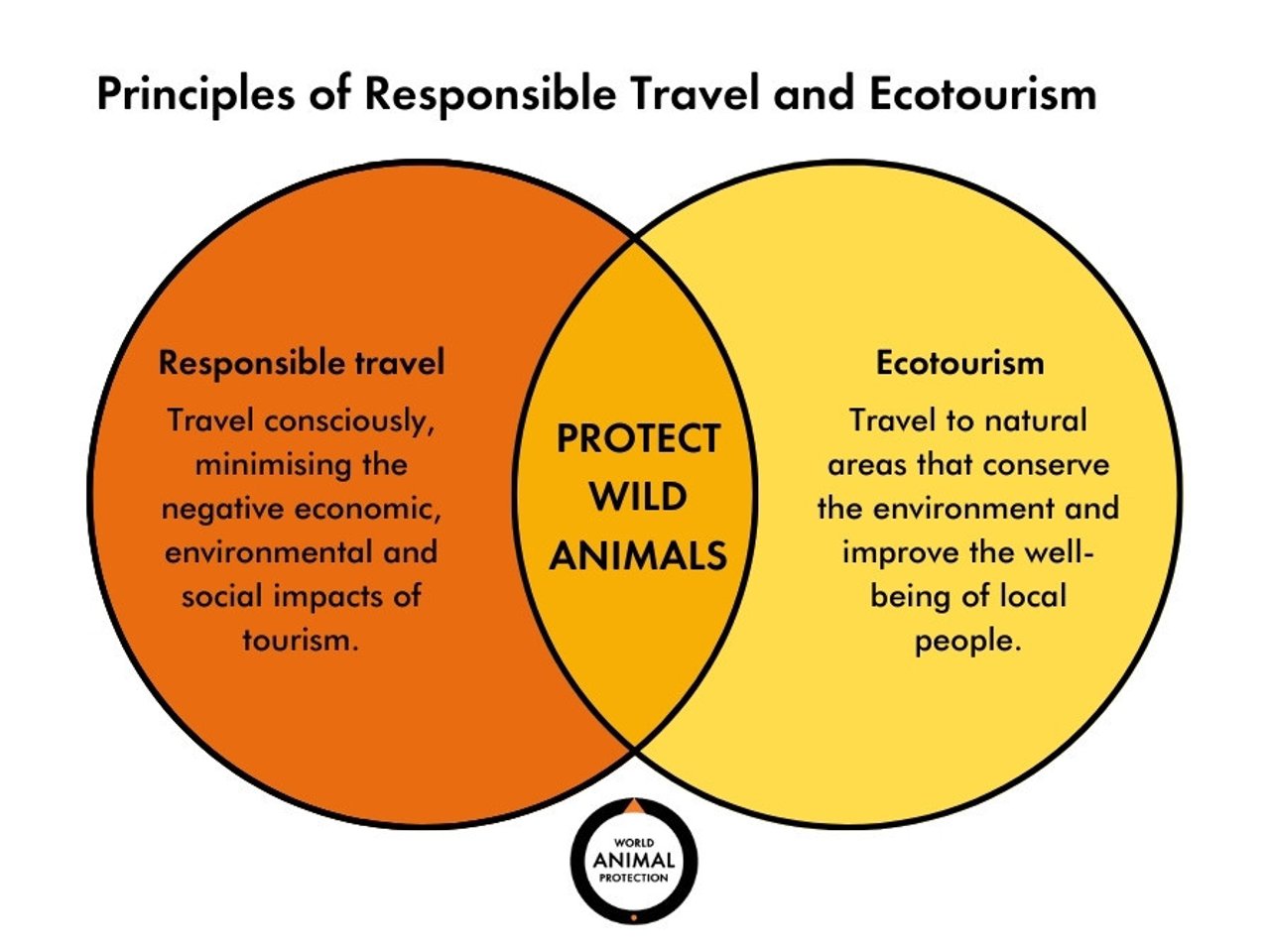
A primary objective of responsible nature tourism is the conservation of natural resources. This encompasses protecting biodiversity, preserving habitats, and mitigating the negative impacts of human activity on delicate ecosystems.
1.1. Funding Conservation Initiatives
Nature tourism can generate crucial financial resources for conservation projects. Revenue from park entrance fees, tour operator contributions, and visitor donations can be channeled into habitat restoration, anti-poaching efforts, and scientific research.
1.2. Promoting Sustainable Practices
By encouraging responsible behavior among tourists and tour operators, nature tourism can minimize environmental damage. This includes promoting low-impact activities, reducing waste, and supporting eco-friendly accommodations.

1.3. Raising Awareness of Environmental Issues
Nature tourism provides a platform for educating visitors about the importance of conservation and the threats facing natural environments. Experiential learning can foster a deeper appreciation for nature and inspire individuals to adopt more sustainable lifestyles.
1.4. Empowering Local Communities in Conservation
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for long-term success. Nature tourism can provide economic incentives for communities to protect their natural resources, empowering them to become stewards of their environment.

Beyond conservation, nature tourism aims to educate visitors about the natural world, fostering a deeper understanding of ecological processes and the interconnectedness of life.
2.1. Enhancing Knowledge of Biodiversity
Nature tourism offers opportunities to observe and learn about diverse plant and animal species in their natural habitats. Guided tours and interpretive programs can provide valuable insights into the ecology and behavior of wildlife.
2.2. Understanding Ecological Processes
Through experiential learning, visitors can gain a better understanding of ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, food webs, and ecosystem dynamics. This can lead to a greater appreciation for the complexity and fragility of natural systems.
2.3. Promoting Environmental Ethics
Nature tourism can instill a sense of environmental responsibility by highlighting the importance of ethical interactions with nature. This includes respecting wildlife, minimizing disturbance, and avoiding the exploitation of natural resources.
2.4. Fostering Scientific Inquiry
Nature tourism can support scientific research by providing access to remote and diverse ecosystems. Tourist observations and data collection can contribute to scientific understanding of natural phenomena.
Nature tourism can serve as a catalyst for economic development in rural and remote areas, providing alternative livelihoods and reducing reliance on unsustainable practices.
3.1. Creating Employment Opportunities
Nature tourism generates employment opportunities in various sectors, including tour guiding, hospitality, transportation, and handicrafts. This can provide much-needed income for local communities and reduce poverty.
3.2. Supporting Local Businesses
Nature tourism can stimulate the growth of local businesses, such as restaurants, souvenir shops, and accommodation providers. This can contribute to the diversification of local economies and reduce dependence on single industries.
3.3. Generating Revenue for Infrastructure Development
Revenue from nature tourism can be invested in infrastructure development, such as roads, trails, and visitor centers. This can improve access to natural areas and enhance the visitor experience.
3.4. Promoting Sustainable Economic Practices
Nature tourism can encourage the adoption of sustainable economic practices, such as organic farming, eco-craft production, and community-based tourism. This can contribute to the long-term economic and environmental sustainability of local communities.
Nature tourism can play a vital role in preserving and promoting the cultural heritage of indigenous and local communities, particularly those with strong connections to the natural environment.
4.1. Supporting Indigenous Tourism Initiatives
Indigenous tourism initiatives can provide opportunities for communities to share their cultural knowledge and traditions with visitors. This can promote cultural understanding and generate income for indigenous communities.
4.2. Protecting Sacred Sites and Cultural Landscapes
Nature tourism can contribute to the protection of sacred sites and cultural landscapes that are important to indigenous and local communities. This includes respecting traditional land use practices and avoiding activities that could damage cultural heritage.
4.3. Promoting Cultural Exchange and Understanding
Nature tourism can facilitate cultural exchange between visitors and local communities, fostering mutual respect and understanding. This can help to break down cultural barriers and promote intercultural dialogue.
4.4. Recognizing the Value of Traditional Ecological Knowledge
Nature tourism can highlight the value of traditional ecological knowledge, which can provide valuable insights into sustainable resource management and conservation. This knowledge can be integrated into conservation and tourism management practices.
Nature tourism offers opportunities for recreation and personal growth, providing visitors with a chance to connect with nature and escape the stresses of modern life.
5.1. Promoting Physical and Mental Health
Spending time in nature has been shown to have numerous physical and mental health benefits, including reducing stress, improving mood, and boosting immune function. Nature tourism provides opportunities to engage in outdoor activities and experience the restorative power of nature.
5.2. Fostering a Sense of Awe and Wonder
Experiencing the beauty and grandeur of natural landscapes can evoke a sense of awe and wonder, which can have a profound impact on personal well-being. Nature tourism provides opportunities to witness breathtaking scenery and encounter diverse wildlife.
5.3. Providing Opportunities for Adventure and Challenge
Nature tourism can offer opportunities for adventure and challenge, such as hiking, kayaking, and wildlife viewing. These activities can promote personal growth and self-discovery.
5.4. Enhancing Spiritual Connection with Nature
For many people, nature tourism provides an opportunity to connect with nature on a spiritual level. This can involve seeking solitude in nature, participating in nature-based rituals, or simply appreciating the beauty and tranquility of the natural world.
While nature tourism offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that must be addressed to ensure its sustainability. These include:
Over-tourism: Excessive visitor numbers can damage fragile ecosystems and disrupt wildlife behavior.
The objectives of nature tourism are multifaceted and interconnected. Achieving a balance between conservation, education, economic development, cultural preservation, and recreation is crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability of this form of tourism. This requires a collaborative approach involving governments, tour operators, local communities, and tourists themselves. By embracing responsible practices and prioritizing the protection of natural and cultural heritage, nature tourism can contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.



