“`html
Quintana Roo: A Tapestry of Natural Treasures
Quintana Roo: A Tapestry of Natural Treasures
Quintana Roo, Mexico’s easternmost state, is a land of breathtaking beauty and abundant natural resources. Nestled on the Yucatan Peninsula, it boasts a unique blend of terrestrial and marine ecosystems, attracting millions of visitors each year. Beyond the sun-kissed beaches and vibrant tourist hubs, lies a complex and delicate web of interconnected natural wonders. This article delves into the diverse natural resources of Quintana Roo, exploring their significance, challenges, and the importance of sustainable management.
The Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System: A Submerged Paradise
One of Quintana Roo’s most prized possessions is its section of the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, the second-largest barrier reef in the world. This underwater marvel stretches along the coast, providing vital habitat for countless marine species. Coral reefs are more than just beautiful; they act as natural breakwaters, protecting coastlines from erosion and storm surges. They also support a thriving fishing industry and contribute significantly to the local economy through tourism.
Coral Reef Biodiversity

The reef is home to a staggering diversity of marine life, including hundreds of species of fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and marine mammals. Colorful parrotfish graze on algae, while majestic sea turtles navigate the intricate coral structures. The reef’s health is crucial for maintaining this biodiversity, but it faces numerous threats, including climate change, pollution, and unsustainable fishing practices.
Threats to the Reef
Coral bleaching, caused by rising sea temperatures, is a major concern. Pollution from coastal development and agricultural runoff introduces harmful chemicals and nutrients into the water, further stressing the reef. Overfishing disrupts the delicate balance of the ecosystem, allowing algae to proliferate and smother corals. Efforts to protect the reef include establishing marine protected areas, promoting sustainable tourism practices, and implementing stricter regulations on fishing and development.
The Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve: A Terrestrial and Aquatic Sanctuary
South of Tulum lies the Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage Site encompassing a vast expanse of tropical forests, wetlands, and coastal ecosystems. This protected area showcases the incredible biodiversity of Quintana Roo, providing habitat for endangered species like jaguars, manatees, and spider monkeys.
Tropical Forests and Wetlands
The reserve’s forests are a mosaic of diverse vegetation, including mangroves, savannas, and tropical deciduous forests. These ecosystems play a crucial role in regulating water cycles, storing carbon, and providing habitat for wildlife. The wetlands, including lagoons and marshes, are vital breeding grounds for birds and fish.
Freshwater Cenotes: Windows to the Underground World
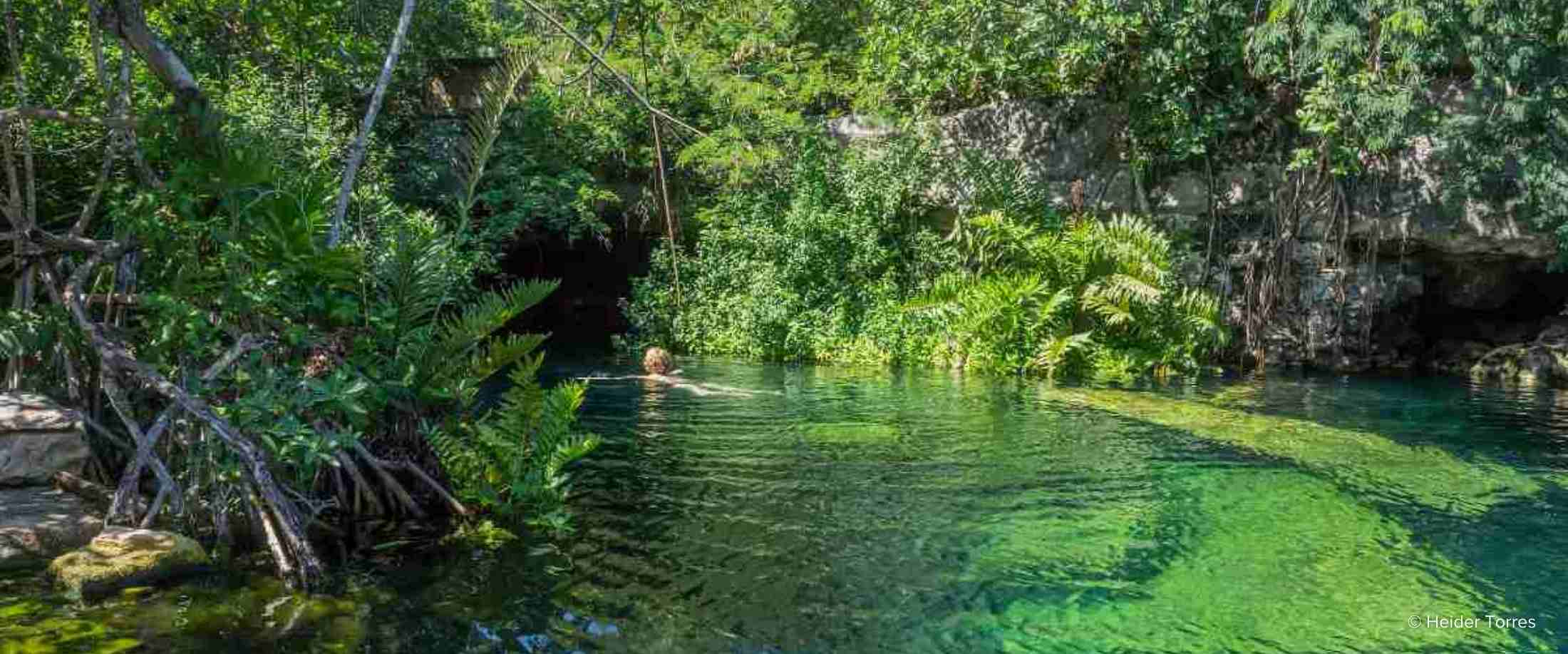

Quintana Roo is renowned for its cenotes, natural sinkholes that reveal the region’s extensive underground river system. These freshwater pools are not only visually stunning but also ecologically significant, providing habitat for unique aquatic species and serving as vital sources of freshwater. The cenotes are interconnected, forming a vast network that influences the region’s hydrology and coastal ecosystems.
The Importance of Freshwater
The availability of freshwater is a critical issue in Quintana Roo. The region relies heavily on groundwater resources, which are vulnerable to contamination from pollution and saltwater intrusion. The cenotes and underground rivers are essential for replenishing these resources, highlighting the need for careful management and conservation. The rapid development of tourism has put a strain on fresh water resources, and the need for sustainable practices is more critical than ever.
Coastal Ecosystems: Mangroves, Beaches, and Lagoons
Quintana Roo’s coastline is a dynamic and diverse environment, characterized by mangroves, sandy beaches, and coastal lagoons. These ecosystems are interconnected and play a vital role in protecting the shoreline, providing habitat for wildlife, and supporting local communities.
Mangrove Forests
Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees that thrive in coastal wetlands. They act as natural barriers against erosion, filtering pollutants and providing nursery habitat for fish and crustaceans. Mangroves also play a critical role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change. Unfortunately, mangrove forests are under threat from coastal development, deforestation, and pollution.
Sandy Beaches and Dunes
The pristine beaches of Quintana Roo are a major tourist attraction. These sandy ecosystems provide habitat for shorebirds and sea turtles, and they also protect the coastline from erosion. Dunes, which are formed by windblown sand, act as natural barriers against storm surges and sea-level rise.
Coastal Lagoons
Coastal lagoons are shallow bodies of water separated from the open sea by barrier islands or sandbars. These ecosystems are highly productive, providing habitat for a variety of fish, birds, and invertebrates. They also play a role in nutrient cycling and water filtration. The lagoons are sensitive to pollution and changes in water salinity, highlighting the need for careful management.
Terrestrial Biodiversity: Forests and Wildlife
Beyond the coastal ecosystems, Quintana Roo boasts a rich terrestrial biodiversity, with tropical forests and a variety of wildlife species. The region’s forests are home to jaguars, ocelots, spider monkeys, and a wide array of bird species.
The Mayan Forest
The Mayan Forest, which covers a significant portion of the Yucatan Peninsula, is a biodiversity hotspot. This forest is home to a variety of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region. The Mayan Forest is also culturally significant, as it has been inhabited by Mayan people for thousands of years.
Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife conservation is a critical issue in Quintana Roo. Many species are threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Efforts to protect wildlife include establishing protected areas, promoting ecotourism, and implementing community-based conservation programs.
Challenges and Sustainable Management
Quintana Roo’s natural resources face numerous challenges, including rapid tourism development, climate change, pollution, and unsustainable resource use. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive and integrated approach to sustainable management.
Tourism and Development
Tourism is a major driver of the economy in Quintana Roo, but it also poses significant environmental challenges. The rapid development of hotels, resorts, and infrastructure has led to habitat loss, pollution, and increased pressure on natural resources. Sustainable tourism practices, such as ecotourism and responsible resource use, are essential for mitigating these impacts.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change is a major threat to Quintana Roo’s natural resources. Rising sea levels, increased storm intensity, and coral bleaching are already impacting the region. Adapting to these changes requires investing in coastal protection, promoting climate-resilient infrastructure, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Pollution and Waste Management
Pollution from sewage, industrial waste, and agricultural runoff is a major concern in Quintana Roo. Improving waste management infrastructure, implementing stricter regulations on pollution, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices are essential for protecting water quality and ecosystem health.
Community Involvement and Education
Community involvement and education are crucial for sustainable management. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, raising awareness about environmental issues, and promoting sustainable livelihoods are essential for long-term success.
Conclusion
Quintana Roo’s natural resources are a treasure trove of biodiversity and ecological significance. From the vibrant coral reefs to the lush tropical forests, the region’s ecosystems are interconnected and vital for the well-being of local communities and the planet. Sustainable management of these resources is essential for ensuring their long-term health and resilience. By embracing responsible tourism, protecting natural habitats, and engaging local communities, Quintana Roo can continue to be a model for sustainable development and conservation.
“`



