Absolutely! Here’s a 3000-word article about four natural resources, formatted with headings as requested:
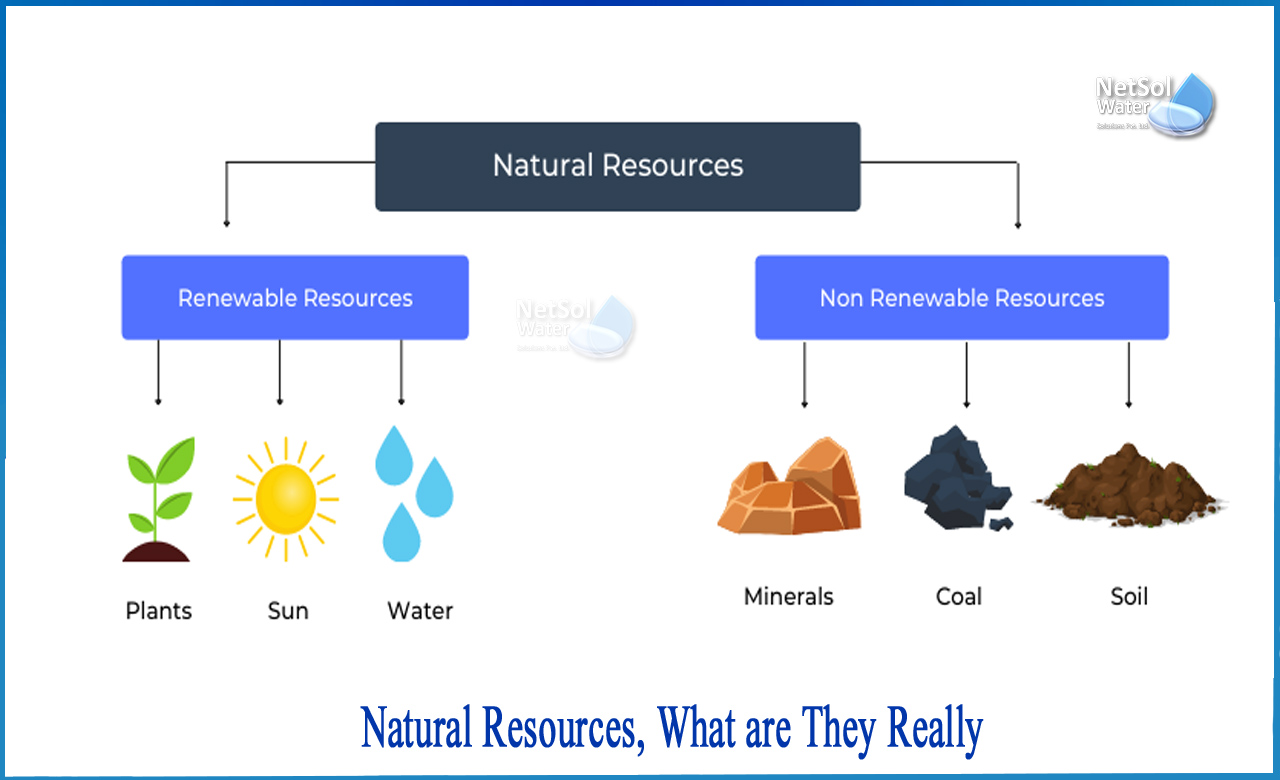
The Earth, our shared home, is a treasure trove of natural resources. These resources, vital for our survival and progress, are materials or substances occurring in nature that can be exploited for economic gain. Understanding their significance and ensuring their sustainable management is crucial for the well-being of present and future generations. Let’s delve into four essential natural resources: water, forests, minerals, and fossil fuels.
Water: The Elixir of Life
Water, the most fundamental of all resources, is indispensable for all living organisms. It covers approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface, yet only a tiny fraction is readily available as freshwater for human use. This scarcity, coupled with increasing demand, makes water a precious and vulnerable resource.
The Water Cycle and its Importance
The water cycle, a continuous process of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, replenishes freshwater sources. Understanding this cycle is essential for water resource management. Evaporation, driven by solar energy, transforms liquid water into vapor, which rises and cools, forming clouds. Precipitation, in the form of rain, snow, or hail, returns water to the Earth’s surface, replenishing rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
Challenges to Water Resources
Pollution: Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and untreated sewage contaminate water bodies, rendering them unusable.
Sustainable Water Management
Conservation: Reducing water consumption through efficient irrigation, leak detection, and water-saving appliances.
Forests: The Lungs of the Earth
Forests, vast ecosystems covering approximately 31% of the Earth’s land surface, play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. They are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, regulate climate, and provide numerous resources.
Ecological Significance of Forests

Carbon Sequestration: Forests absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide, mitigating climate change.
Threats to Forests
Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture, logging, and infrastructure development.
Sustainable Forest Management
Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees to restore degraded forests and create new forests.
Minerals: The Foundation of Industry
Minerals, naturally occurring inorganic substances with a definite chemical composition and crystal structure, are essential for various industries, from construction and manufacturing to electronics and energy.
Types of Minerals and their Uses

Metallic Minerals: Iron, aluminum, copper, gold, and silver, used in construction, transportation, and electronics.
Challenges of Mineral Extraction
Environmental Degradation: Mining operations can cause soil erosion, water pollution, and habitat destruction.
Sustainable Mineral Management
Recycling and Reuse: Recovering and reusing minerals from electronic waste and other sources.
Fossil Fuels: Powering the Modern World
Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, are formed from the remains of ancient organisms. They have powered the industrial revolution and continue to be a major source of energy.
The Role of Fossil Fuels
Electricity Generation: Fossil fuels are used to generate electricity in power plants.
Environmental Impacts of Fossil Fuels
Climate Change: Burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming.
Transition to Sustainable Energy
Renewable Energy Sources: Investing in solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy.
In conclusion, these four natural resources—water, forests, minerals, and fossil fuels—are fundamental to our existence and prosperity. Sustainable management of these resources is crucial for ensuring a healthy and prosperous future for all. By adopting responsible practices, promoting conservation, and investing in sustainable technologies, we can safeguard these vital resources for generations to come.



